In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, safeguarding patient information is paramount. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) compliance is a crucial aspect of ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic protected health information (ePHI). One of the foundational steps toward HIPAA compliance is conducting a thorough HIPAA Risk Assessment.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the various types of risk assessments, provide a step-by-step approach to conducting a HIPAA risk assessment, and highlight the importance of connecting this assessment to your overall security program.
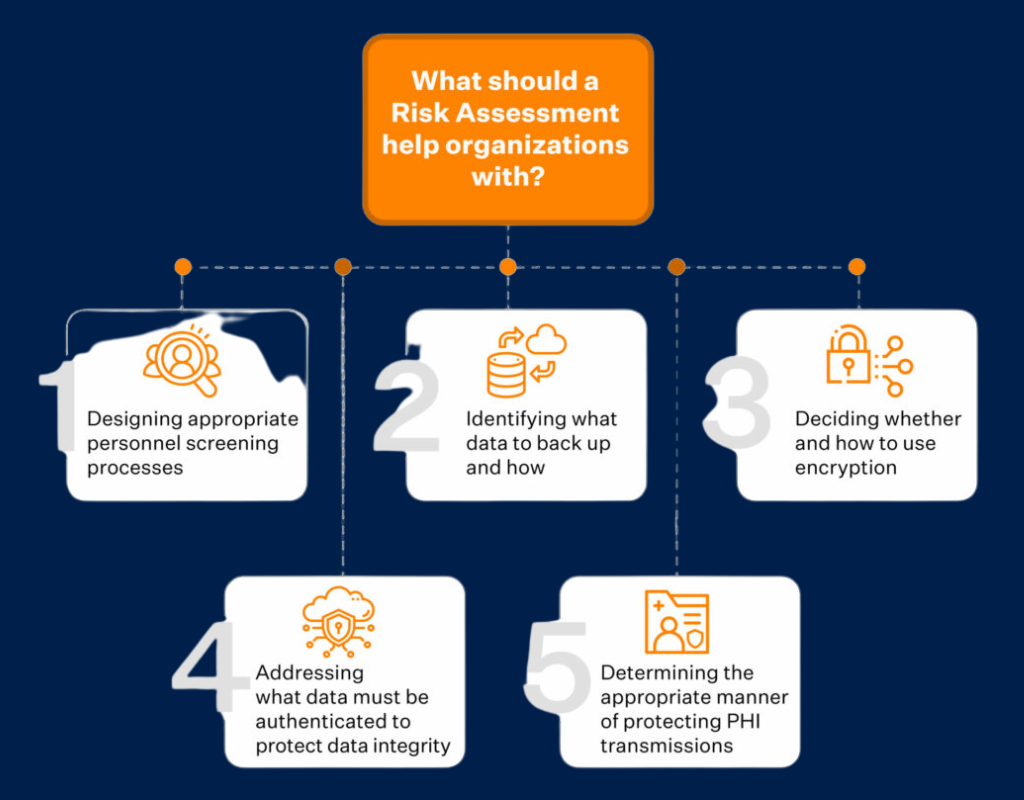
Types of Risk Assessments
1. Security Risk Assessment (SRA):
Conducting an SRA involves identifying and analyzing potential risks to ePHI. This includes assessing vulnerabilities in the physical, technical, and administrative aspects of your healthcare organization.
2. Privacy Risk Assessment:
A privacy risk assessment focuses on the policies and procedures in place to protect patient privacy. It evaluates how well your organization adheres to HIPAA’s Privacy Rule, ensuring that patient rights and confidentiality are maintained.
3. Third-Party Risk Assessment:
In today’s interconnected healthcare ecosystem, assessing risks associated with third-party vendors and business associates is critical. Ensure that your partners comply with HIPAA regulations to mitigate potential breaches.
8 Steps for Conducting a HIPAA Risk Assessment

Step 1: Establish a Risk Analysis Team:
Assemble a dedicated team with expertise in information security, privacy, and the specific operations of your healthcare organization.
Forming a dedicated and interdisciplinary team is the foundation of a successful risk assessment. Ensure representation from IT, compliance, legal, and operations. This team will bring diverse perspectives to identify and analyze potential risks comprehensively.
Step 2: Identify ePHI:
Clearly define and document where ePHI is stored, processed, or transmitted within your organization.
A precise understanding of where electronic protected health information (ePHI) resides is crucial. Document the locations, systems, and processes that handle ePHI, whether it’s in electronic health records (EHRs), databases, or even portable devices.
Step 3: Identify and Document Potential Threats and Vulnerabilities:
Conduct a comprehensive analysis of potential risks, including natural disasters, human error, and cyber threats. Identify vulnerabilities in your systems and processes.
Comprehensive threat identification involves considering a spectrum of possibilities—from natural disasters to cybersecurity threats. Document vulnerabilities such as outdated software, weak access controls, or physical risks like unsecured areas where ePHI is stored.
Step 4: Assess Current Security Measures:
Evaluate existing security measures and controls in place, ensuring they align with HIPAA requirements. Evaluate the effectiveness of existing security measures and controls in place. This includes firewalls, encryption, access controls, and policies. Determine if these measures align with HIPAA requirements and if they adequately protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI.
Step 5: Determine the Likelihood and Impact of Threats:
Assess the probability and potential impact of identified threats to prioritize risk mitigation efforts. Quantify the likelihood and potential impact of each identified threat. This step helps prioritize risks for mitigation efforts. High-impact, high-likelihood risks may need immediate attention, while lower-impact risks may be addressed in subsequent phases.
Step 6: Evaluate Security Controls:
Determine the effectiveness of current security controls in mitigating identified risks. Examine the efficiency of your security controls in mitigating identified risks. This involves assessing whether the controls in place adequately address vulnerabilities and reduce the likelihood and impact of potential threats.
Step 7: Assess the Risk:
Combine the likelihood and impact assessments to determine the overall risk level for each identified threat.Combine the likelihood and impact assessments to determine the overall risk level for each identified threat. This step helps in categorizing risks as high, medium, or low, guiding the prioritization of mitigation strategies.
Step 8: Document Findings:
Thoroughly document the entire risk assessment process, including findings, recommendations, and action plans. Documenting the entire risk assessment process is crucial for accountability and compliance. Include detailed findings, risk levels, and recommendations for mitigating each identified risk. This documentation serves as a reference for ongoing risk management.
Implement Risk Mitigation Strategies:
Develop and implement strategies to mitigate identified risks, ensuring ongoing compliance with HIPAA regulations. Develop and implement strategies to address and mitigate identified risks. This may involve enhancing security controls, updating policies and procedures, or investing in new technologies. Prioritize actions based on the severity of risks and available resources.
Regularly Review and Update:
Conduct periodic reviews and updates to the risk assessment to account for changes in technology, regulations, or organizational structure. A HIPAA risk assessment is not a one-time activity. Regular reviews and updates are essential to account for changes in technology, regulations, or the organization’s structure. Keep the risk assessment dynamic and aligned with the evolving healthcare landscape.
By diligently following these 10 steps, healthcare organizations can not only meet regulatory requirements but also strengthen their overall security posture. A proactive and comprehensive approach to risk assessment contributes to a culture of continuous improvement and resilience in the face of emerging threats. Remember, safeguarding patient information is an ongoing commitment, and a well-executed risk assessment is a cornerstone of this commitment.
Also check out: Top 10 Consulting Firms in the USA
Also check out: Understanding What is HIPAA Law: Why You Need to Follow It
Connecting a Risk Assessment to Your Security Program
A HIPAA risk assessment should not be a standalone activity but an integral part of your organization’s broader security program. Here’s how you can seamlessly integrate the findings into your security initiatives:
1. Develop a Risk Management Plan:
Create a comprehensive risk management plan based on the assessment findings, outlining strategies to address and mitigate identified risks.
2. Employee Training and Awareness:
Ensure that employees are well-versed in the risks identified and the corresponding measures in place to mitigate them. Regular training sessions can enhance awareness and compliance.
3. Incident Response Plan:
Integrate the results of the risk assessment into your incident response plan. Clearly define the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident, minimizing potential damage and ensuring a swift response.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Auditing:
Implement continuous monitoring processes and regular audits to track the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies. This proactive approach helps in identifying emerging threats and adapting security measures accordingly.
5. Documentation and Reporting:
Maintain thorough documentation of risk assessment activities and regularly report to key stakeholders, fostering a culture of transparency and accountability.
Conclusion
Conducting a HIPAA risk assessment is not just a compliance requirement but a proactive measure to safeguard patient information in an increasingly digital healthcare landscape. By following the 10 steps outlined and integrating the findings into your overall security program, you not only meet regulatory obligations but also fortify your organization against potential threats. Stay vigilant, stay compliant, and most importantly, stay committed to the security and privacy of your patients’ information.
Remember, a robust HIPAA risk assessment isn’t just a checkbox—it’s your organization’s commitment to excellence in healthcare data security.

